The utilization of PGP encryption on the darkweb is prevalent for various reasons. Primarily, PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) is an open-source encryption protocol that is renowned for its robust security features, rendering it highly suitable for preserving anonymity and confidentiality. Its asymmetric encryption algorithm enables individuals to transmit encrypted data, ensuring that only the intended recipient can decrypt and access the information. Additionally, PGP offers a dependable means of verifying the authenticity of digital communication through digital signatures, which prevents tampering and impersonation. This feature is particularly crucial in darknet online activities where trust and authenticity are vital. Coupled with its easy implementation and widespread availability of PGP software, its popularity on the darkweb is understandable, as it caters to the need for secure and private communication within this ecosystem.
Some quick history on PGP
PGP was originally developed in 1991 by Phil Zimmermann, a renowned cryptographer and advocate for robust privacy protection. Zimmermann's primary objective was to provide individuals with a powerful encryption solution that would guarantee their privacy in the face of mounting concerns about surveillance and data interception.

Initially, Zimmermann encountered legal obstacles due to restrictions on the export of cryptographic software from the United States. Nevertheless, PGP gained widespread acceptance as users recognized its effectiveness and potential to safeguard sensitive information.
In 1997, PGP was transformed into a commercial product when it was acquired by Network Associates Inc. (now McAfee). Despite its commercial status, a free implementation of PGP, known as "GNU Privacy Guard" (GnuPG or GPG), is still available and widely used by individuals and organizations.
In recent years, the significance of securing communications against surveillance and data breaches has become increasingly apparent. PGP continues to be a widely adopted encryption standard, empowering individuals and organizations to protect their sensitive information and communicate securely.
Understanding PGP Message Encryption: Ensuring Communication Security
In an era where the utmost importance is placed on confidentiality and data protection, the utilization of PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) message encryption has emerged as a dependable solution for ensuring the security of electronic communication. This article delves into the fundamental principles of PGP encryption, emphasizing its significance in safeguarding sensitive information and preserving privacy.
How Does PGP Encryption Work?
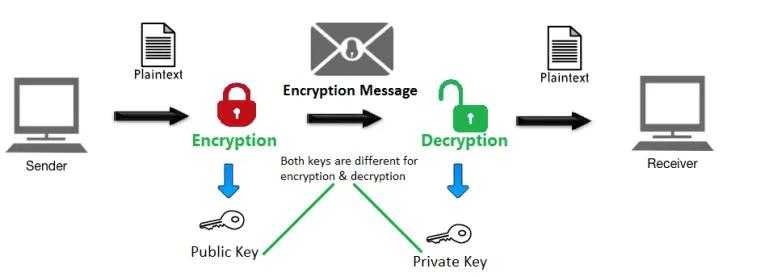
The foundation of asymmetric encryption is rooted in the utilization of public and private key pairs, which are at the core of PGP encryption.
Asymmetric Encryption: The Power of Key Pairs
Asymmetric encryption is a cryptographic methodology that employs two distinct yet mathematically correlated keys, namely the public key and the private key. The sender employs the recipient's public key to encrypt the message, thereby guaranteeing that only the recipient, who possesses the corresponding private key, can decrypt it. This technique provides a high degree of security, as the message remains inaccessible to anyone without the private key.
PGP Key Management
The process of generating and safeguarding key pairs is of utmost importance. Key generation entails the creation of a public-private key pair, whereby the private key is retained by the owner and the public key is disseminated to others. It is imperative to ensure the protection of private keys, as any breach may result in the unauthorized decryption of encrypted messages. To this end, users are advised to store their private keys in secure storage, such as encrypted hardware devices or password-protected keyrings.
Sharing your public PGP key
In order to establish secure communication, it is imperative for individuals to exchange public keys. This can be accomplished through manual sharing of the public key via secure channels such as trusted messaging applications. Alternatively, key servers can be utilized as repositories for public keys.
Encryption Using Recipient's Public Key
The originator employs the recipient's public key to encrypt the message, resulting in a ciphertext that is exclusively decipherable by the recipient's private key. This approach ensures that the message remains indecipherable to unauthorized parties, even if it is intercepted during transmission.
Digital Signatures for Integrity and Authentication
PGP additionally enables the utilization of digital signatures, which fulfill two fundamental objectives: guaranteeing the integrity of the message and authenticating the identity of the sender.
Ensuring Message Integrity
By utilizing their private key, the sender affixes a signature to the message, thereby generating an assurance that the recipients can authenticate by means of the sender's public key. This procedure ensures that the message remains unchanged throughout the transmission process.
Verifying the Sender's Identity
Digital signatures offer a guarantee concerning the legitimacy of the sender. Through the validation of the signature utilizing the sender's public key, recipients can place reliance on the origin of the message.
PGP-Compatible Tools: Widening Adoption and Ease of Use
OpenPGP is an open, standardized version of PGP that allows for interoperability between different software and platforms. This enhances flexibility and encourages wider adoption. With OpenPGP, users can choose from a variety of software implementations that support the standard.
There exist several prevalent PGP encryption tools that provide dependable and user-friendly cryptographic solutions. One notable tool is GNU Privacy Guard (GPG), an open-source and free implementation of PGP that enjoys widespread usage across various platforms. GPG offers robust encryption capabilities and can be seamlessly integrated with email clients, file systems, and other applications. Another well-received option is Kleopatra, which forms part of the Gpg4win software suite and presents a graphical interface for managing PGP keys and encrypting files. Furthermore, Enigmail is a popular PGP encryption tool that is specifically tailored for integration with the Mozilla Thunderbird email client, thereby facilitating secure email communication. These encryption tools, among others, have gained popularity due to their strong security features, ease of use, and compatibility with diverse operating systems.
Strong Passphrases for Private Keys
It is imperative that users utilize robust and distinctive passphrases for their private keys. The implementation of a strong passphrase serves as an extra measure of security to deter unauthorized entry. It is highly advisable to incorporate a blend of uppercase and lowercase letters, numerical digits, and special characters.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it can be asserted that PGP message encryption plays a pivotal role in securing private communication, protecting sensitive information, and ensuring authenticity. By employing robust encryption algorithms, efficient key management practices, and digital signatures, PGP offers a reliable solution for individuals seeking privacy and security in their electronic communications.
It is imperative to note that implementing appropriate security measures, such as utilizing strong passphrases, regularly updating keys, and staying informed about vulnerabilities, are crucial in maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of encrypted communication. Furthermore, exploring alternative encryption tools and protocols can provide users with additional options for secure communication, based on their specific needs and preferences.
Over the course of its evolution, PGP encryption has emerged as a trustworthy and highly respected method for safeguarding electronic communication. With ongoing advancements and continuous efforts to address security concerns, PGP encryption remains a viable choice for individuals and organizations looking to protect their important and confidential data. These factors have contributed to the immense popularity of PGP across the dark web, particularly in darknet markets.

